Excerpted from Eight Steps to Successfully Implement Blended Learning in Your Classroom. Download it today.
Having technology in your classroom can be a fantastic thing. It has the potential to expose your students to a world of information, hand’s on projects and game based learning, like our middle school science games. In order to maximize your classroom experience with blended learning it is critical to have a school culture that supports technology integration.
Getting Administrators & Parents On Board With Blended Learning
 Making the shift from traditional learning to blended learning is daunting and impacts every stakeholder in a school community, including leaders, teachers, IT staff, students, and parents. As a result, the journey from old to new, from traditional to blended, must be a shared journey—one in which all stakeholders are engaged and all voices are heard.
Making the shift from traditional learning to blended learning is daunting and impacts every stakeholder in a school community, including leaders, teachers, IT staff, students, and parents. As a result, the journey from old to new, from traditional to blended, must be a shared journey—one in which all stakeholders are engaged and all voices are heard.
For a blended learning initiative to be successful long-term, decisions cannot be top down or device driven. Instead leaders must carefully consider why they want to make a shift to blended learning and how that shift will benefit members of the school community. To get administrators and parents on board, use these two approaches.
Administrators
Administrators may hesitate to invest in blended learning because of cost or lackluster results. Overcome their concerns with detailed research and data that show blended learning’s past successes and your plans to implement the teaching model in the classroom.
Administrators also want hard numbers about projected academic performance. They prefer financial documents, implementation plans, and blended learning examples. The more data and documentation you can provide, the more likely your blended learning proposal will receive approval.
Parents
Parents care about academic performance on a more personal level—everyone wants their child to succeed. They want to know how their child is performing academically, and what you’re teaching in the classroom. They also desire to learn how to help their child improve test scores and study habits.
To reach parents, talk through how blended learning will motivate their student to learn and excel, they will back the initiative. Your conversation could prompt them to become advocates on your behalf and secure support from administrators, other teachers, and peer parents.
Establishing A Blended Learning Culture In The Classroom
 Blended Learning Universe marks the importance of culture in blended learning success. The organization states:
Blended Learning Universe marks the importance of culture in blended learning success. The organization states:
Blended learning can sustain a bad culture or help create a new one. Culture is especially useful — or toxic — in blended programs because blended learning goes hand in hand with giving students more control and flexibility. If students lack the processes and cultural norms to handle that agency, the shift toward a personalized environment can backfire.
Start With Clear & Honest Communication
As such, your blended learning culture sets the tone for classroom instruction and assignments. It fosters the right attitudes in students, inside and outside the classroom. Culture can affect parents, too, causing them to encourage, rather than frustrate, their students’ blended learning activities.
To establish culture inside the classroom, begin with clear and honest communication with your students. Set expectations for your blended learning program, whatever it encompasses—classroom projects, edgames, student teams, at-home assignments, et cetera.
Use The “TRICK” Acronym
Also employ “TRICK,” an acronym suggested by Esther Wojcicki and Lance Izumi, authors of “Moonshots in Education: Launching Blended Learning in the Classroom.” The acronym stands for trust, respect, independence, collaboration, and kindness. When your classroom embodies those five traits, students learn, grow scholastically and personally, and desire to help their fellow students.
Outside the classroom, you should also focus on communication, this time with parents. Just because you got their initial buy-in doesn’t mean your work is done. Let parents know how their kids are enjoying and improving thanks to your new blended learning environment. Remember that some parents may not be familiar with digital technologies and tools, especially if you teach in a rural or underserved area. Share basic information about blended learning with these parents, and offer opportunities for them to experience it in the classroom. Showing parents how blended learning works can better convince them than a letter sent home.
Spread The Culture Across The School Campus
Finally, aim to spread your blended learning culture across the school campus. Your own success with the initiative often sells itself, but you should talk about it, too. Sharing results and personal testimony invites other teachers to participate in blended learning and make a difference in their classrooms.
Learn More About Blended Learning With LoL
Our online educational games at Legends of Learning works perfectly with and seamlessly integrates into blended learning models. For more information, give us a call at 888.585.1317 or contact us online today.
You can download the whole white paper Eight Steps to Successfully Implement Blended Learning in Your Classroom here on the Legends of Learning site.





 While there is great content built off of the NGSS DCI content system available, there is still a wide range of activities that teachers need to take on. Successful implementation requires a multidimensional approach to teaching to be the norm in every science classroom. This requires
While there is great content built off of the NGSS DCI content system available, there is still a wide range of activities that teachers need to take on. Successful implementation requires a multidimensional approach to teaching to be the norm in every science classroom. This requires 
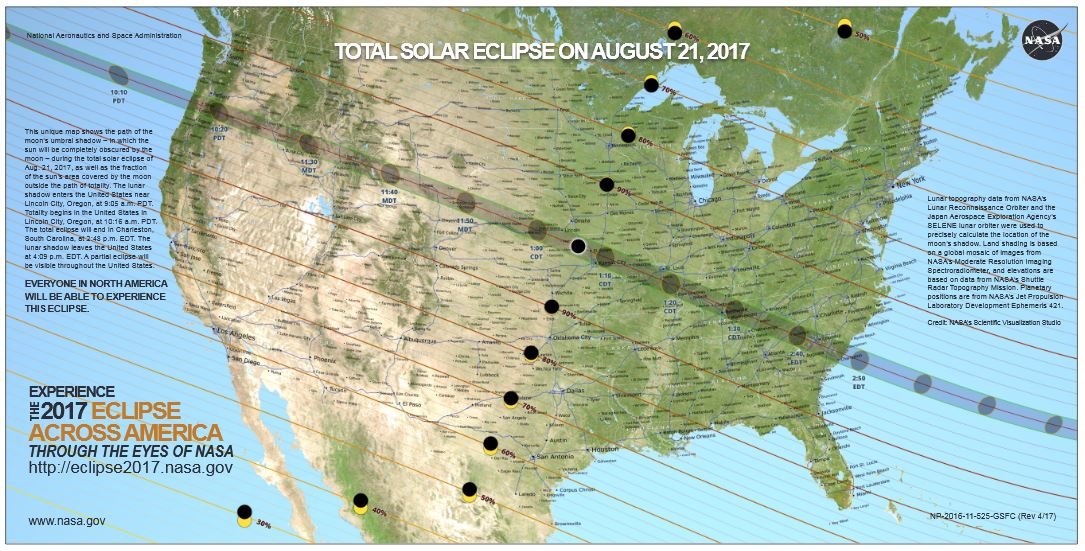
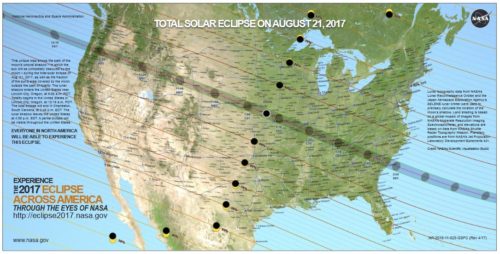

 Making the shift from traditional learning to blended learning is daunting and impacts every stakeholder in a school community, including leaders, teachers, IT staff, students, and parents. As a result, the journey from old to new, from traditional to blended, must be a shared journey—one in which all stakeholders are engaged and all voices are heard.
Making the shift from traditional learning to blended learning is daunting and impacts every stakeholder in a school community, including leaders, teachers, IT staff, students, and parents. As a result, the journey from old to new, from traditional to blended, must be a shared journey—one in which all stakeholders are engaged and all voices are heard.











